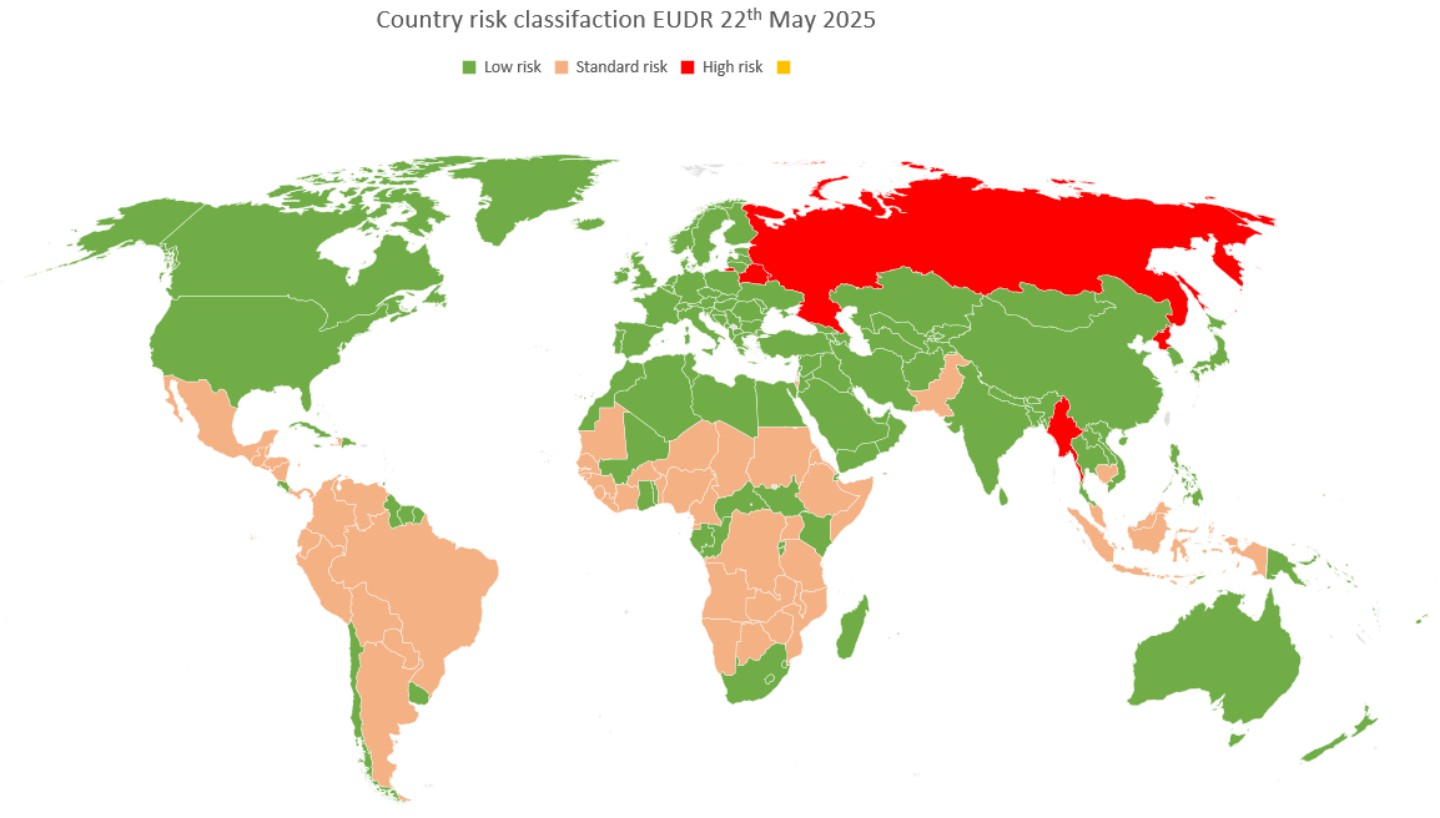
EUDR Countries risk classification
The European Commission has compiled a list in which they have classified all countries worldwide into three risk categories. This classification affects how companies must set up their due diligence system for the European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). This list also gives guidance to the competent authority on the number of checks they must perform.
What does this mean for companies and the competent authorities?
The EUDR requires operators to collect geolocations of source areas of their raw materials. Through these geolocations, it is possible to trace which country the raw materials come from. The implications of the classification vary by risk category:
| Low | Standard | High | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operators | Collect geolocations of all source areas | ||
| Only risk assessment on complexity of supply chain as well as mixing with other raw materials. | Full risk assessment on all assessment criteria from the EUDR. | ||
|
Competent authorities |
1% Check | 3% Check | 9% Check |
Background information
Risk categories
The three risk categories are: low, standard and high risk. When classifying the countries, the following was taken into account:
- The rate of deforestation and forest degradation*;
- The rate of expansion of agricultural land for relevant commodities;
- production trends of relevant raw materials and relevant products.
* Forest degradation is not included in the classification because the source used does not contain sufficient information on forest degradation. However, this will be included in the next update in 2026.
The European Commission uses for (a) the Global Forest Resource Assessments (FRA) and for (b) and (c) the United Nations FAOSTAT database as sources of information.
Classification of countries
A country is classified as low risk if there is:
- no net forest loss between 2015 and 2020, or;
- less than 1,000 hectares per year of forest loss, or;
- a maximum 0.2% average annual forest loss between 2015 and 2020, and;
no more than 70,000 hectares of lost forest cover per year; or; - no expansion of agricultural land associated with EUDR crops, and;
no increase in timber and livestock production, and;
no expansion of total agricultural land.
A country is classified as standard risk if:
- it is not classified as low or high risk;
- an additional assessment does not still classify the countries as high risk. This additional assessment consists of:
- Offset emissions through a contribution to UNFCCC
- EU cooperation on non-deforestation
- National regulations and enforcement
- Availability of relevant data on e.g. human rights, etc.
A country is classified as high risk if:
- it is still classified under high risk via the additional assessment;
- it is subject to UN Security Council or EU Council sanctions on the import or export of the goods and products concerned.